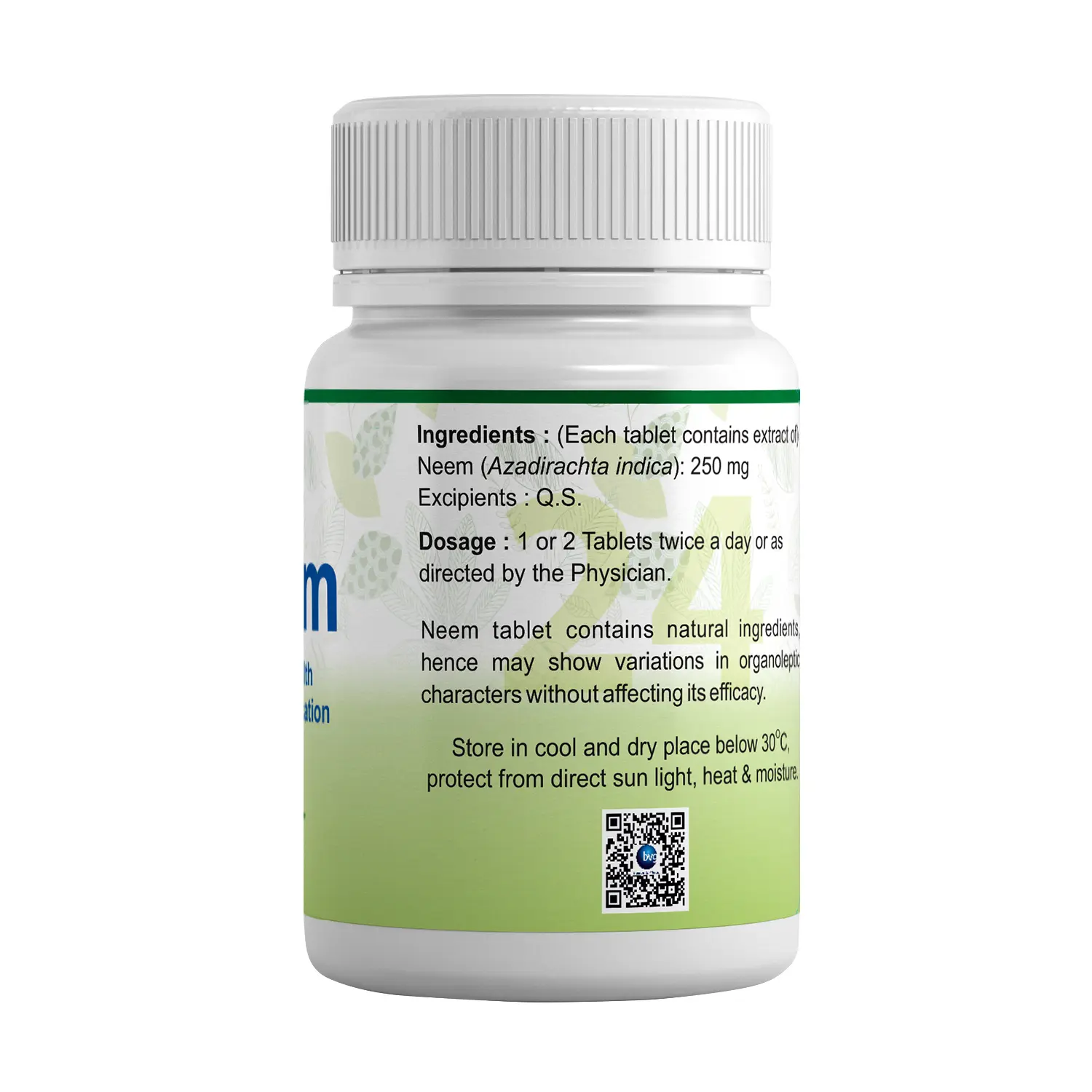
| Anti-bacterial: The antibacterial potential may be due to various phytochemicals like phenols and flavonols. A. indica is the most effective against S. aureus and S. typhiand was moderately effective against Proteus vulgaris and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Anti-oxidant: The neem leaf fractions showed protective, antioxidant effects against oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide. It inhibits oxidation reduces the formation of free radicals and helps to shield the body from oxidative stress.
Anti-ulcer: The extract of neem bark was found to be effective in gastric ulcers, esophageal ulcers, and gastro-duodenal ulcers.
Anti-Pyretic: Neem leaves show a protective effect against fever. Nimbidine is an active ingredient in neem leaves that show antipyretic properties.
Anti-Diabetic: Neem leaf extract provides the best results against blood glucose levels and liver abnormalities. Active components in neem are responsible for modulating the several metabolic pathways in the body responsible for sugar regulation. Liminoids present in neem leaves are the major anti-diabetic agents they are responsible for inhibiting the key carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase.
Renal Protection: Neem leaf extract pre-treatment normalized the levels of serum creatinine, urea, and electrolytes as well as reversed kidney apoptosis and necrosis. This is indicative, that neem leaf extract has the potential to attenuate nephrotoxicity and protect the kidney functions in preclinical studies.
Hepato-protective: Neem is responsible for improving liver function because of the presence of several bioactive components. Hepatoprotective activity is mainly attributed to the presence of rutin and quercitin, responsible for decreasing the necrosis in liver cells. Another important bioactive component present in neem leaves is Azadirachtin-A which helps in decreasing necrosis in hepatic cells and ultimately restoring the liver functions to normal.
Anti-cancer activity: Neem-derived constituents can block cancer growth through diverse biomolecular and cellular mechanisms. Neem phytochemicals suppress the proliferation and growth of cancer cells, induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, interfere with growth factor signalling, inhibit angiogenesis, and decrease tumour cell invasion and migration. These curative powers of the neem tree could be due to the presence of numerous chemical constituents, such as azadirachtin, gedunin, nimbidin, nimbidol, nimbin, salannin, and quercetin, present in various parts of the plant.
Neuroprotective activity: Azadirachta indica elucidates its neuroprotective effect in partial sciatic nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain by its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic potential. The early apoptotic cells were decreased after Azadirachta indica treatment. |























harigovind chaturvedi –
Good herbal product
Dr Shiv Singh –
Good product